Network Flow Metadata
Beta feature
This feature is in beta and may be subject to change in future versions of Enclave. While in beta, this feature doesn't include API endpoints or Portal control and must be manually configured on each system. This page will be updated as the feature enters general availability.
If you have feedback on this feature, please let us know at support@enclave.io.
Introduction¶
Having deeper visibility and insights into your network usage and performance can greatly improve your ability to assess your network security state, troubleshoot and diagnose issues more efficiently, and help you answer questions about your network in real-time. Understanding user access behaviour and knowing what traffic is flowing through your network enables you to discover threats quickly and assist in validating that your intended network security policies are in place.
To facilitate this level of network visibility and monitoring your network requires tools that can efficiently generate valuable metadata from your network traffic in real-time. This metadata can then be analysed to provide the visibility and insights described above.
Network metadata-based tools such as NetFlow and IPFIX are well known in the network industry. These tools and protocols all share a common architecture:
Flow Exporter – Generates network flow metadata and exports the metadata towards one or more flow collectors.
Flow Collector - responsible for reception, storage and pre-processing of flow metadata received from a flow exporter.
Flow Analysis Application - analyses flow metadata in the context of reporting, intrusion detection, traffic profiling, network performance, user access behaviour, etc.
Traditionally flow exporters are implemented on network devices such as routers, switches and firewalls. End-to-end encrypted overlay networks such as Enclave make it impossible for these network devices to extract metadata from the actual underlying application traffic as they can only “see” the already encrypted overlay packets. This is where the Enclave Network Flow Metadata feature comes into play.
Enclave Network Flow Metadata¶
The Enclave Network Flow Metadata feature provides the functionality to generate network flow metadata on traffic going over the encrypted Enclave overlay. Enclave Network Flow Metadata implements an IPFIX exporter. IPFIX is an IETF protocol that provides a universal standard for the export and collection of IP flow metadata. The Enclave IPFIX exporter conforms to RFC 7011 and RFC 7012.
IPFIX Collectors¶
The Enclave IPFIX exporter generates network flow metadata and sends it to one or more collectors using the IPFIX protocol. The collectors are responsible for storage and processing of the flow metadata received from the Enclave IPFIX exporter, and they typically also provide the flow analysis and insights applications. Since the Enclave Network Flow Metadata feature implements a standards-based IPFIX exporter, it should be compatible with any collector that supports the IPFIX standard. We have tested integration with the following 3rd party collectors:
ElastiFlow, Plixer Scrutinizer, Noction, Paessler PRTG IPFIX Analyzer
IPFIX Templates¶
Enclave implements IPFIX templates for exporting IPv4/IPv6 TCP, IPv4/IPv6 UDP, raw IPv4/IPv6, and ICMPv4 flow information.
Limitation¶
The IPFIX specification defines three transport protocols that can be used to transport flow information from the exporter to the collector: SCTP, TCP and UDP. Our research found that all IPFIX collectors support UDP almost exclusively as their transport protocol. As such, we have focused our efforts on implementing UDP as the transport protocol for the Enclave exporter.
Configuration¶
To enable and configure the Enclave Network Flow Metadata feature on your system, you will need to edit your Enclave configuration file. Follow these steps:
Step 1: Stop the Enclave process¶
On Windows, right click on the Enclave desktop app icon, click on Universe and then click on Stop.
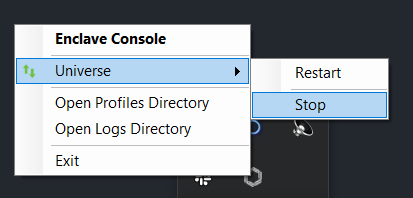
You can also stop Enclave in a Windows command prompt using enclave stop
C:\> enclave stop
On Linux you can use sudo enclave stop or sudo systemctl stop enclave
Step 2: Edit your Enclave configuration file¶
On Windows the Enclave configuration file is located at C:\Program Files\Enclave Networks\Enclave\Agent\profiles\Universe.profile. We recommend you edit the configuration file through the Enclave desktop app by clicking on the settings icon in the top left corner of the Enclave application and selecting Edit profile configuration file..., or you can manually edit the file.
Note
When manually editing the configuration file you will need to run your editor, e.g. Notepad, as Administrator.
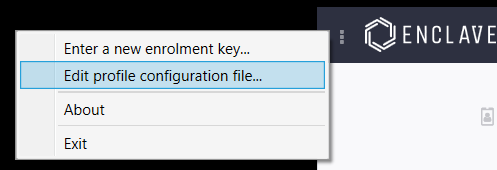
On Linux the Enclave configuration file is located at /etc/enclave/profiles/Universe.profile and can be edited using your preferred editor, e.g.
sudo nano /etc/enclave/profiles/Universe.profile
Step 3: Configure Enclave Network Flow Metadata¶
Enclave Network Flow Metadata is configured using the JSON property FlowMetadata. Under FlowMetadata we provide the following configuration properties and options:
-
IpFixCollectors- A list of zero of more IPFIX collector endpoints in the string format "Udp/Collector IP Address:Port" e.g.Udp/172.16.1.100:4739. The example specifies thatUDPis the transport protocol to use,172.16.1.100is the IP address of the IPFIX collector and the collector is listening on UDP port4739. You can specify multiple IPFIX collectors and Enclave will forward IPFIX flow information to all configured collectors. By default no exporters are configured. -
Direction- Valid string values areBoth,SendingToPeerandReceivedFromPeer. The default value if not specified isBoth.IPFIX supports single direction flow information per data record. This means a normal bidirectional flow e.g. a TCP session, will generate two IPFIX data records, one for ingress information and a second for egress information. This is the default behaviour and what will be expected when you configure
Bothas the direction.In certain circumstances this might not be ideal; imagine you are running Enclave on System A and System B, both have IPFIX enabled and is monitoring a TCP session between them. With the default
Bothdirection, System A will export both ingress and egress data, while System B will also export both ingress and egress data. This means you end up with 4 flow records for a single TCP session. With theSendingToPeerandReceivedFromPeerdirection options you can limit flow information export to either egress information or ingress information respectively.Note
There is one exception to the direction setting. Frames dropped due to violation of Trust Requirements or Access Control Rules will always generate an IPFIX record and be exported, irrespective of the direction setting. For example, even if you have configured
ReceivedFromPeer, if an outgoing frame to a remote Enclave peer is dropped due to either a Trust Requirements or an Access Control Rules violation, Enclave will still report on this egress record. -
Interval- The interval in milliseconds at which Enclave will generate and export interim IPFIX flow records. IfIntervalis set to 0, then Enclave will not generate interim flow records, but will only generate and export flow records at the end of each flow. Interval should be either 0, or a multiple of 60000 (1 minute) as Enclave only processes interim records on a 1-minute frequency. The default value is 0. -
Enabled- Valid values aretrueorfalse. Used to enable or disable the Enclave IPFIX exporter feature. The default value istrue.Warning
If you have enabled IPFIX through this setting but have not configured a collector in
IpFixCollectors, then the Enclave IPFIX exporter will effectively be disabled. You need to both set enabled to true and have a collector configured for the Enclave collector to function.
To add the IPFIX configuration options, add the JSON settings at the bottom of the Enclave configuration file you opened in Step 2. The following example enables IPFIX and adds a single IPFIX collector with IP address 172.16.1.100 that is listing on UDP port 4739. Enclave will be configured to export both ingress and egress flow information, and interim IPFIX flow records will be generated every 60 seconds (60000 milliseconds).
"FlowMetadata":{
"IpFixCollectors": [
"Udp/172.16.1.100:4739"
],
"Direction": "Both",
"Interval": 60000,
"Enabled": true
}
Save the configuration file.
Step 4: Start the Enclave process¶
Once you have saved the IPFIX configuration you can start the Enclave process again. On Windows, right click on the Enclave desktop app icon, click on Universe and then click on Start.
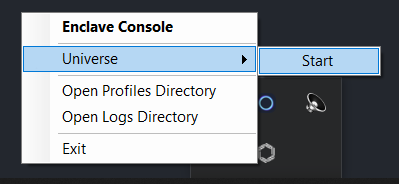
You can also start Enclave in a Windows command prompt using enclave start
C:\> enclave start
On Linux you can use sudo enclave start or sudo systemctl start enclave
Enclave should now be running with the IPFIX exporter feature enabled and you should start receiving flow records in your IPFIX collector.
Having problems? Contact us at support@enclave.io